Introduction
Cloud modernization is transforming how businesses operate in today’s digital age. Imagine your business infrastructure as an aging house that’s served you well but is struggling to keep up with modern demands. Just as you’d renovate that house to incorporate new technologies and efficiency improvements, cloud modernization transforms your outdated IT systems into a state-of-the-art digital powerhouse.
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, cloud modernization isn’t just another IT buzzword – it’s essential for business survival. The growing emphasis on cloud modernization is evident as U.S. software spending is projected to rise by 10.7% in 2025, driven largely by cloud innovation and AI integration. As your trusted partner in digital transformation and cloud modernization, MN Service Providers is here to guide you through this crucial journey.
Understanding Cloud Modernization
Let’s break down what cloud modernization really means. Think of it as giving your entire IT infrastructure a smart home upgrade – not just moving furniture around, but fundamentally improving how everything works together. Unlike simple cloud migration (which is like relocating to a new house without changing anything), cloud modernization transforms your applications and processes to fully leverage cloud capabilities.
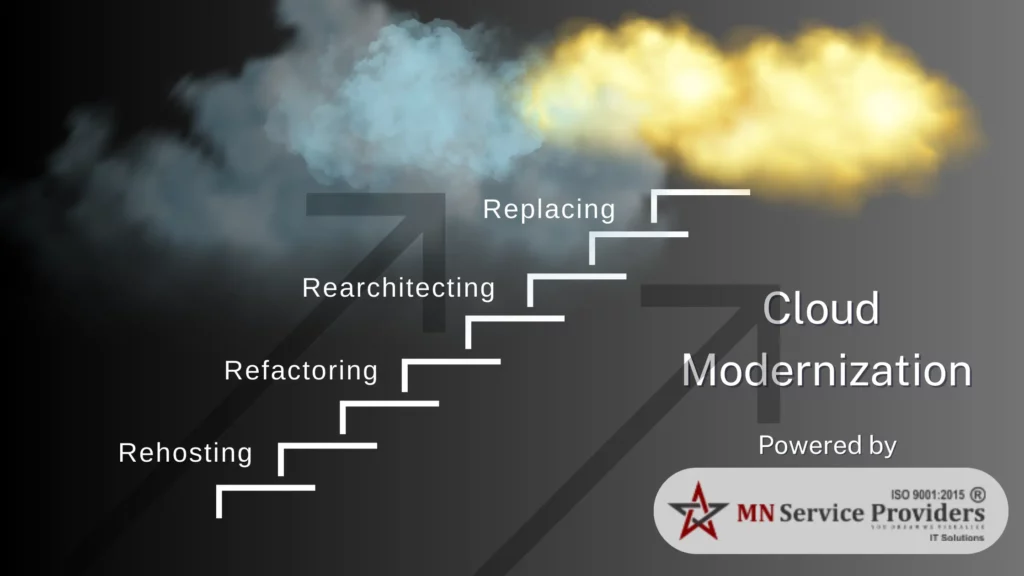
There are several approaches to cloud modernization:

Rehosting (lift and shift)
Rehosting is the most straightforward approach to modernization, often called “lift and shift.” It involves moving applications from on-premise servers to the cloud with minimal or no changes to the underlying code. While it offers quick wins in terms of cost reduction and infrastructure scalability, it doesn’t fully tap into the cloud’s native benefits like auto-scaling or serverless architecture.
Organizations often choose this method to quickly decommission legacy systems and establish a cloud footprint. It’s typically used as a stepping stone for more advanced modernization strategies in the future.
Refactoring (optimizing code)
Refactoring involves modifying existing application code to better suit the cloud environment without changing its core functionality. The goal is to optimize performance, enhance security, and reduce costs by making use of cloud-native tools and services such as managed databases or message queues.

This approach can significantly improve efficiency and agility, especially when dealing with monolithic applications that need to become more modular.
However, it requires a deeper understanding of both the existing codebase and cloud architecture. It strikes a balance between minimal disruption and meaningful performance gains.

Rearchitecting (rebuilding for cloud-native features)
Rearchitecting is the most transformative and often the most complex strategy. It involves redesigning an application’s architecture from the ground up to leverage cloud-native features such as microservices, containers, serverless computing, and managed services.
This enables businesses to achieve high availability, better scalability, faster deployments, and more agile development cycles.
While the upfront investment in time and resources is higher, the long-term benefits in terms of flexibility and innovation are substantial. Rearchitecting is ideal for organizations committed to a cloud-first or cloud-native strategy.
Replacing (switching to new solutions)
Replacing, sometimes referred to as repurchasing, means abandoning legacy applications entirely and adopting new, often SaaS-based, solutions. For instance, a company might replace its on-premise CRM system with a cloud-native platform like Salesforce. This approach is useful when the existing system no longer meets business needs or when the cost of modernization outweighs the cost of a new solution.
It allows organizations to quickly adopt industry best practices and benefit from frequent updates and built-in security. However, it also requires change management and training to ensure smooth user adoption.
Assessing Your Business Needs
How do you know it’s time for cloud modernization? Watch for these red flags:
- Your applications take too long to update or deploy
- Scaling up during peak times is a manual, painful process
- Unexpected spikes in cloud expenses can catch your team off guard
- Staying ahead of security threats can often feel like you’re always one step behind.
According to research, 59% of organizations now have dedicated FinOps teams to manage cloud costs and optimization www.forbes.com, showing just how crucial proper cloud management has become.
Crafting a Cloud Modernization Strategy
Creating your cloud modernization roadmap is similar to organizing a long-distance journey—it requires planning, checkpoints, and flexibility. You need to:
- Know your starting point (current infrastructure)
- Define your destination (modernization goals)
- Plan your route (implementation strategy)
- Prepare for detours (risk management)
Set SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) for your modernization journey. For example: ” Cut application deployment time in half within a six-month window.”
Choosing the Right Cloud Environment
The cloud environment you select must reflect your operational priorities and long-term goals.
- Public cloud: Like renting a fully-furnished apartment
- Private cloud: Like owning your own house
- Hybrid cloud: a balanced blend of flexibility and control
Leading providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud each offer unique advantages. At MN Service Providers, we help you evaluate which platform best suits your specific requirements.
Analyzing and Auditing Existing Systems
Before modernization begins, conduct a thorough inventory of your current systems. This process reveals:
- Applications that can be modernized immediately
- Systems requiring gradual transformation
- Dependencies that need special attention
- Technical debt to be addressed
Rearchitecting for the Cloud
Moving to microservices architecture is like breaking down a huge department store into specialized boutiques – each focused on doing one thing extremely well. This approach offers:
- Better scalability
- Easier maintenance
- Faster updates
- Improved resilience
Focus on Security During Cloud Modernization
Security isn’t just a checkbox – it’s the foundation of your modernized infrastructure. Recent studies show that 70% of organizations plan to increase their cloud security investments in 2025.
Implement:
- Zero-trust architecture
- Automated security testing
- Continuous compliance monitoring
- Regular security audits
Data Modernization for the Cloud
Preparing your data for modernization is like organizing a massive library:
- Catalog everything you have
- Clean and standardize the information
- Establish clear categorization systems
- Create backup and recovery procedures
Re-skilling and Empowering Your Team
Adapting to a cloud-centric ecosystem means your team must acquire new technical proficiencies. Invest in:
- Technical training
- Process education
- Change management workshops
- Leadership development
Partner with experts like MN Service Providers to help bridge skill gaps during transition.
Partnering with the Right Vendors
Choosing the right cloud modernization partner is like selecting a general contractor for a major home renovation. MN Service Providers brings extensive experience in:
- Cloud architecture design
- Implementation and migration
- Security and compliance
- Ongoing maintenance and support
Look for partners who:
- Have proven experience in your industry
- Offer comprehensive service portfolios
- Foster solid partnerships with leading cloud vendors for smoother integrations and support.
- Provide clear communication and transparency
Executing a Phased Cloud Modernization Plan
Start small and scale up – this approach helps minimize risks and maximize learning opportunities. A typical phased approach includes:
Phase 1: Planning and Assessment (2-4 weeks)
- Infrastructure evaluation
- Goal setting
- Team alignment
Phase 2: Pilot Project (1-2 months)
- Select non-critical application
- Test modernization approach
- Gather feedback and adjust
Phase 3: Scaled Implementation (3-6 months)
- Roll out to more applications
- Implement learned best practices
- Monitor and optimize
Monitoring and Testing During Modernization
Set up comprehensive monitoring systems to track:
- Application performance
- Resource utilization
- User experience
- Cost metrics
Managing Change Across the Organization
Remember, cloud modernization is as much about people as it is about technology. According to change management studies, projects with excellent change management are six times more likely to meet objectives.
Key strategies include:
- Regular stakeholder updates
- Clear communication of benefits
- Training and support programs
- Celebration of quick wins
Optimizing Costs During Cloud Modernization
Smart cost management strategies include:
- Right-sizing resources
- Implementing auto-scaling
- Using reserved instances
- Monitoring idle resources
Studies show that organizations waste an average of 30% of their cloud spend. MN Service Providers helps you avoid this pitfall through proper planning and optimization.
Ensuring Business Continuity
Maintain business operations during modernization by:
- Creating detailed rollback plans
- Implementing redundant systems
- Testing disaster recovery procedures
- Maintaining clear communication channels
Leveraging Automation and AI
Automation is your secret weapon for efficiency. Implement:
- Automated testing
- CI/CD pipelines
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- AI-powered monitoring
Improving Application Performance
Post-modernization optimization should focus on:
- Regular performance testing
- User experience monitoring
- Load balancing
- Caching strategies
Case Studies: Success Stories
Let’s examine some real-world cloud modernization success stories that showcase the transformative power of well-executed strategies:
- Experian’s Data Silo Integration: The credit scoring giant successfully modernized its legacy applications by moving to AWS, achieving:
- Improved collaboration among data scientists
- Enhanced ability to scale during peak marketing campaigns
- Better security and regulatory compliance
- 50% reduction in deployment efforts through Azure Private Link
- Significant improvement in data processing capabilities
- Capital One’s Complete Cloud Transformation: In an ambitious eight-year project, Capital One modernized 2,000 applications on AWS, resulting in:
- Dramatic reduction in disaster recovery time
- 50% reduction in transaction errors
- Significant decrease in development environment build time
- Enhanced customer experience through AI-powered services
- Improved security and operational resilience
Conclusion
Successful cloud modernization is a journey, not a destination. With proper planning, the right partners, and a strategic approach, you can transform your organization’s digital capabilities while minimizing risks and maximizing returns.
Ready to start your cloud modernization journey? Contact MN Service Providers today for a free consultation and discover how we can help you achieve your digital transformation goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Cloud modernization is the process of updating legacy applications and infrastructure to take full advantage of cloud-native capabilities, improving scalability, performance, and cost-efficiency.
Cloud migration is simply moving applications to the cloud “as-is,” while cloud modernization involves optimizing and transforming applications to leverage cloud-native features and modern architectures.
Modern cloud computing refers to the latest cloud technologies and practices, including containerization, microservices, serverless computing, and DevOps, that enable organizations to build and deploy scalable, flexible applications.
Lift and shift (rehosting) involves moving applications to the cloud without changes, while refactoring means restructuring and optimizing the application’s code to better utilize cloud-native features and improve performance.
Cloud migration is the process of moving your digital business operations – including data, applications, and IT processes – from on-premises servers to the cloud.
Melvin C Varghese is an author with more than 8 years of expertise in DevOps, SEO and SEM. His portfolio blogs include a Digital Marketing blog at https://melvincv.com/blog/ and a DevOps blog at https://blog.melvincv.com/. He is married with 2 small kids and is a simple person who eats, sleeps, works and plays. He loves music, comedy movies and the occasional video game.